2-D and 3-D Plots
Line Plots
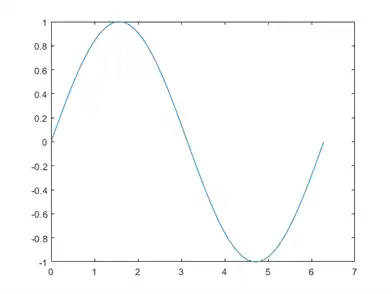
To create two-dimensional line plots, use the plot function. For example, plot the value of the sine function from 0 to 2π:
x = 0:pi/100:2*pi; y = sin(x); plot(x,y)
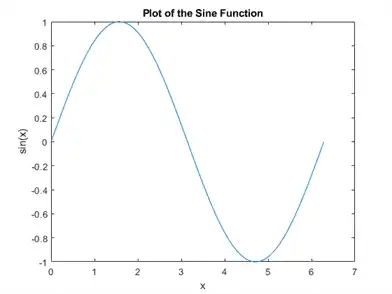
You can label the axes and add a title.
xlabel('x')
ylabel('sin(x)')
title('Plot of the Sine Function')
By adding a third input argument to the plot function, you can plot the same variables using a red dashed line.
plot(x,y,'r--')
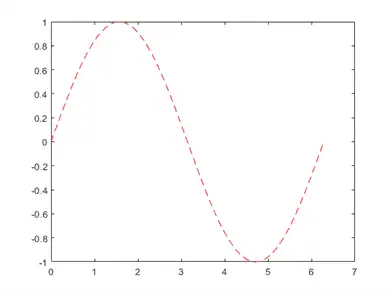
'r--' is a line specification. Each specification can include characters for the line color, style, and marker. A marker is a symbol that appears at each plotted data point, such as a +, o, or *. For example, 'g:*' requests a dotted green line with * markers.
Notice that the titles and labels that you defined for the first plot are no longer in the current figure window. By default, MATLAB® clears the figure each time you call a plotting function, resetting the axes and other elements to prepare the new plot.
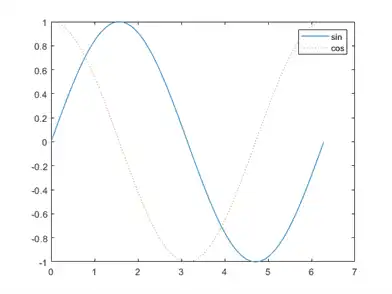
To add plots to an existing figure, use hold on. Until you use hold off or close the window, all plots appear in the current figure window.
x = 0:pi/100:2*pi;
y = sin(x);
plot(x,y)
hold on
y2 = cos(x);
plot(x,y2,':')
legend('sin','cos')
hold off
3-D Plots
Three-dimensional plots typically display a surface defined by a function in two variables, z = f(x,y) .
To evaluate z, first create a set of (x,y) points over the domain of the function using meshgrid.
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-2:.2:2); Z = X .* exp(-X.^2 - Y.^2);
Then, create a surface plot.
surf(X,Y,Z)
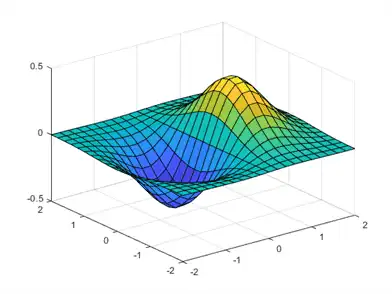
Both the surf function and its companion mesh display surfaces in three dimensions. surf displays both the connecting lines and the faces of the surface in color. mesh produces wireframe surfaces that color only the lines connecting the defining points.
Subplots
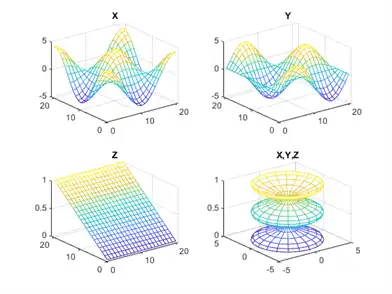
You can display multiple plots in different subregions of the same window using the subplot function.
The first two inputs to subplot indicate the number of plots in each row and column. The third input specifies which plot is active. For example, create four plots in a 2-by-2 grid within a figure window.
t = 0:pi/10:2*pi;
[X,Y,Z] = cylinder(4*cos(t));
subplot(2,2,1); mesh(X); title('X');
subplot(2,2,2); mesh(Y); title('Y');
subplot(2,2,3); mesh(Z); title('Z');
subplot(2,2,4); mesh(X,Y,Z); title('X,Y,Z');