Introduction to Boost converters
Boost converters are mainly used to step up the input voltage to desired values, A boost converters operate on switching mode for the purpose of dc to dc conversion in which output voltage is always greater than input voltage given.it is also known as step up converter this name originated from process of step up transformer where input is stepped up to desire level, On the basis of law of conversion of energy the input power should be equal to output power considering there are no losses.
Input power (Pinput) = output power (Poutput)
As we know that the output voltage is greater than input voltage Vout>Vin,therefore input current will be more than output current. Vin < Vout and Iin >Iout
Principle of operation of Boost converter
Working principal of boost converter is based on inductor used at input side of circuit is generally use to make barrier for sudden varying of input current ,it stores the energy in form of magnetic energy when the switch is in off condition and gets discharge when switch is closed. The capacitor used at the output side of the circuit considered as large enough that the time constant of RC circuit in the output stage is high. The large time constant compared to switching period represents that a constant output
voltage Vo(t) = Vo(constant)
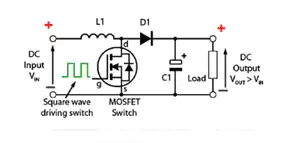
The boost converter can be structured in two different ways-
Open loop converter – Boost converter said to be a open loop converter when there is no feedback between input and output, therefore the open loop converter cannot be regulated.
Closed loop converter – Boost converter is said to be a close loop converter when there is feedback between input and output, therefore the close loop converter can be regulated.
Control of close Boost Converter is utilized to acquire a steady DC output voltage. The output voltage is decided by the switching frequency and duty cycle. In close loop converter process the output voltage is compared a set voltage and the error is decreased by controlling the switching pulse .The fundamental activity is if the error value is certain the obligation cycle is diminished and if the error is negative the D cycle is expanded by proceeding with the procedure ceaselessly the yield voltage is looked after steady.
Example:
2.1 Design and simulation of a boost converter
A boost converter supplies a resistive 20? load at 240V from a 96V DC supply. The switching frequency is 100 kHz. A filtering inductor and smoothing capacitor are used to limit the peak-to-peak ripple in inductor current and output voltage, respectively.
Solution :-
Mathematical solution
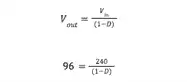
After solving above equation we get value of D as:-


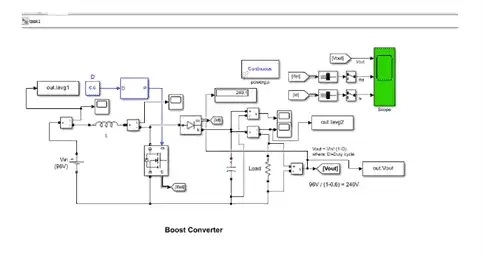
2.2(b)MATLAB simulation of the circuit is given below as :-
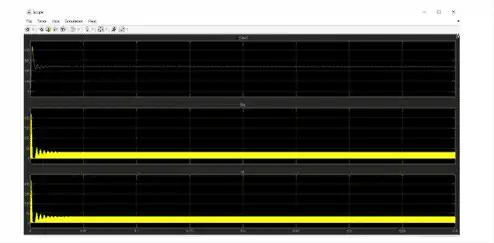
Simulation Output:-


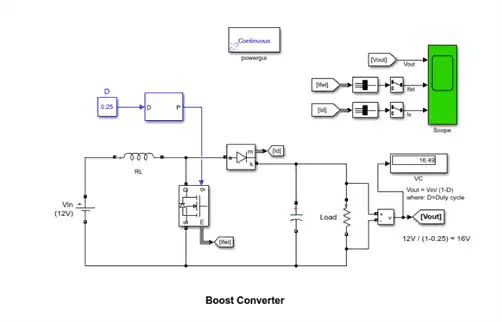
2.1(d)Open loop boost converter is simulated on the parameters given below:-
|
Vin |
12 v |
|
Vout( desired) |
16v |
|
L(Inductance) |
1.5e-3 |
|
Capacitance |
250e6 |
|
Switching frequency |
5000 hz |
Value of D obtained from the given formula theoretical is given below:-
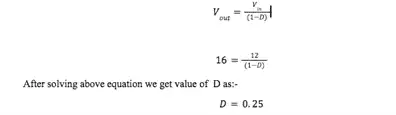
We got the output voltage nearer to the desired voltage of 16 volt
Now, simulating closed loop boost converter with same parameters as provided previously :-
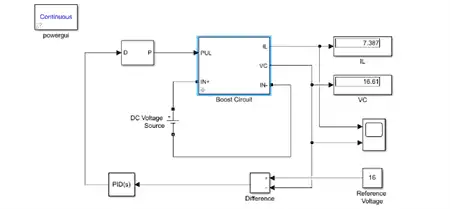
We got the output voltage nearer to the desired voltage of 16 volt as 16.61,we observed that there are certain limitations of this circuit. The output voltage in this circuit is not regulated it varies for different load resistances. This can be improved by adding a feedback circuitry which helps in regulating the output voltage.