Introduction to Boost converters
Boost converters are mainly used to step up the input voltage to desired values, A boost converters operate on switching mode for the purpose of dc to dc conversion in which output voltage is always greater than input voltage given.it is also known as step up converter this name originated from process of step up transformer where input is stepped up to desire level, On the basis of law of conversion of energy the input power should be equal to output power considering there are no losses.
Input power (Pinput) = output power (Poutput)
As we know that the output voltage is greater than input voltage Vout>Vin,therefore input current will be more than output current. Vin < Vout and Iin >Iout
Example:-
Task 2.2
Performance of a space-vector PWM IGBT inverter-fed induction motor drive.
A Simulink block diagram of the drive system with V/f control referenced above is shown in Figure 1. The corresponding parameters are given in the Appendix.:
PMW inverter is used to fed the induction motor , Universal Bridge Block is used PMW inverter. Our speed controller consists in a PI regulator that produces a slip compensation, which is added to the rotor speed in order to derive the commanded stator voltage frequency. A constant volts per hertz ratio is also applied to the motor. The motor drives a mechanical load characterized by inertia J, friction coefficient B, and load torque TL.
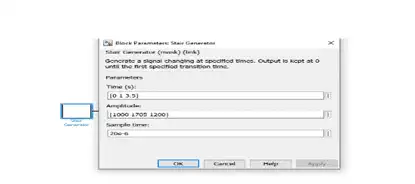
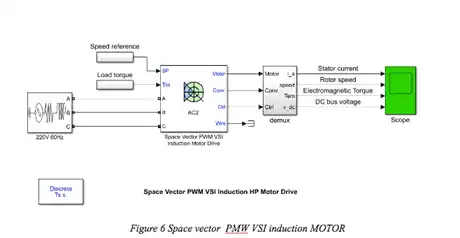
Reference speed defined by user at different time interval is implemented.
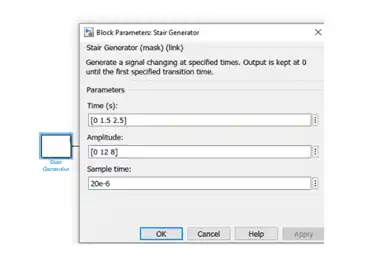
Fixed load torque variations, the timer block is set to [0 1.5 2.5] (s), and the corresponding load torque levels are [0 12 8] Nm.
Simulation Result
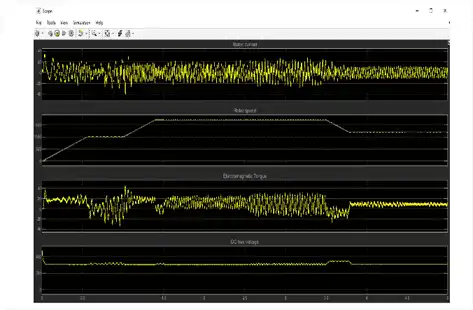
Above circuit is simulated for 5 second as per details problem statement, After running the simulation ,we can observe from the result the output scope of different measuring parameter as the motor stator current, the rotor speed, the electromagnetic torque and the DC bus voltage on the scope, We already initialized the desired speed set point and the torque set point. At time t = 0 s, the speed set point is 1000 rpm. As shown in output waveform, the speed follows precisely the acceleration ramp.
At t = 0.5 s, the full load torque is applied to the motor shaft while the motor speed is still ramping to its final value. This forces the electromagnetic torque to increase to a high value and then to stabilize at 12 N.m once the speed ramping is completed and the motor has reached 1000 rpm.
At t = 1 s, the speed set point is changed to 1700 rpm and the electromagnetic torque reaches again a high
At t = 1.5 s, the mechanical load input from 12N.m to 8 N.m , which leads the electromagnetic torque to stabilize at approximately at 8 N.m shortly after. Note that the DC bus voltage increases since the motor is in the braking mode. This increase is limited by the action of the braking chopper. After 2.5 seconds its again attain previous dc voltage value.
2.2(2)
According to the data provided Voltage =230v, Resistance=0.820, Torque=12Nm, frequency=60Hz
From equation (E) substitute k value.

voltage should be applied to the stator terminals to run the motor at nominal speed for the same load will be 230.1 v
2.2 (3) Solution:
Extraction: a) 2-pole Induction machine electromagnetic torque equation is
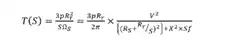
Here Ir represents rotor current,Rr is rotor resistance and Sr is the stator resistance,v represents the machine voltage ,x is leakage reactance , s for slip and f is for supply frequency.




